National Identity
- Motto: God, Honor, Country
- National Anthem: Bolivianos, el hado propicio (Bolivians, a most favorable Destiny), 1851
- National flowers: the Kantuta (Decree of 1924) and Patuj˙ (Decree of 1990)
- Arms of Bolivia: The Bolivian flag today (since 1851) is composed of 3 horizontal stripes - red (people's blood), yellow (mineral wealth) and green (plant wealth), and its center with a blazon showing:
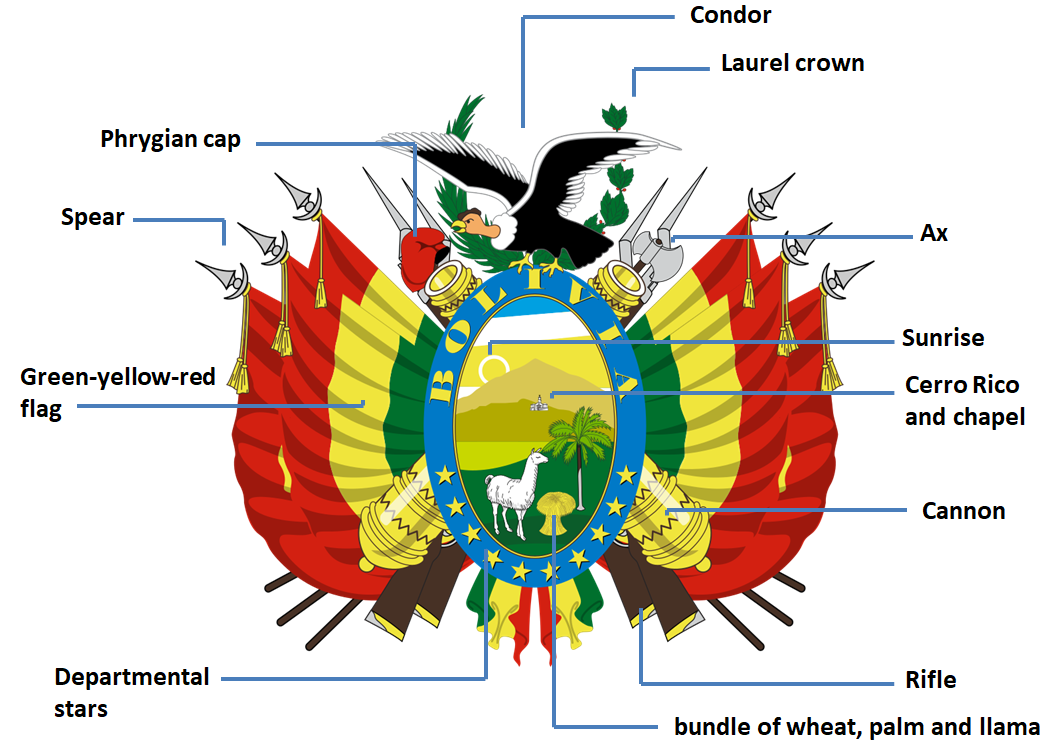
- a condor (national bird)
- a laurel crown (victory and glory) and olive (peace)
- flags placed on each spear, with the colors of Bolivia
- an ax (authority and command)
- cannons, rifles and spears (military)
- a red Phrygian cap (freedom)
- a light blue ellipsis (province of Littoral) containing 10 gold stars (10 departments of Bolivia, including Littoral)
- the Cerro Rico of PotosÝ (wealth)
- the chapel of the Church "Compa˝ia de Jesus" on the Cerro Menor at the foot of Cerro Rico (sacred)
- the bundle of wheat, palm and llama (abundant natural resources)
- sunrise (birth and glory)
Administrative divisions
Bolivia is divided into three major natural geographic areas, each covered by three departments.
Bolivia has two capitals:
- La Paz (seat of executive power)
- Sucre (constitutional capital and seat of legislative power)
Bolivia is divided into 9 departments (Beni, Chuquisaca, Cochabamba, La Paz, Oruro, Pando, Potosi, Santa Cruz and Tarija) who are organized into 112 provinces and 1652 districts. This administrative division is a legacy of the Spanish colonial period (Audiencia de Charcas). The division into departments was inspired by the French model.
The Bolivian state
Bolivia is an independent republic since 1825, which is governed by three main powers:
- the executive,
- the legislature,
- and the judiciary
The president is both head of state and government. He is elected and his term is 5 years. The executive is also assured by the Vice-President, ministers appointed by the president and governors of provinces.
Legislative power is in the hands of the National Congress divided into two chambers: the upper house consists of 27 senators (3 per province) and the lower house consists of 130 deputies.
The judiciary power is guaranteed by the Supreme Court of Justice, headquartered in Sucre, and Supreme Courts in each department district. The Supreme Court of Justice is composed of 12 judges elected by the National Congress for 10 years.
